Poland - Foreign trade
Until recently, foreign trade was a state monopoly under the control of the Ministry of Foreign Trade. After World War II, the orientation of Polish trade shifted from Western and Central European countries to Eastern Europe. This changed with the dissolution of the Soviet-bloc CMEA in 1991. In December of that year, Poland signed an association agreement with the EC (now the EU) and by 2000, 70% of its exports and 61% of its imports were going to EU members. Poland also fosters trade through its membership in the Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA), which includes Hungary, the Czech Republic, and the Slovak Republic.
Poland's export commodities are a mixture of manufactured goods including furniture (7.0%), garments (6.1%), motor vehicles (4.6%), iron and steel (3.9%), and ships (3.3%). Export commodities formed from natural resources include wood(2.5%); coal, lignite, and peat (2.3%); and copper (2.3%). In 2000 Poland's imports were distributed among the following categories:

| Consumer goods | 13.7% |
| Food | 5.0% |
| Fuels | 10.7% |
| Industrial supplies | 33.7% |
| Machinery | 23.8% |
| Transportation | 12.9% |
| Other | 0.2% |
Principal trading partners in 2000 (in millions of US dollars) were as follows:
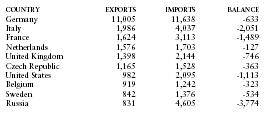
| COUNTRY | EXPORTS | IMPORTS | BALANCE |
| Germany | 11,005 | 11,638 | -633 |
| Italy | 1,986 | 4,037 | -2,051 |
| France | 1,624 | 3,113 | -1,489 |
| Netherlands | 1,576 | 1,703 | -127 |
| United Kingdom | 1,398 | 2,144 | -746 |
| Czech Republic | 1,165 | 1,528 | -363 |
| United States | 982 | 2,095 | -1,113 |
| Belgium | 919 | 1,242 | -323 |
| Sweden | 842 | 1,376 | -534 |
| Russia | 831 | 4,605 | -3,774 |
May I have the latest data? THANKS.