United Arab Emirates - Public finance
A federal budget is prepared according to the UAE's development policy, while each emirate is responsible for municipal budgets and local projects. Conservative public expenditure policies have become more necessary as oil revenues have declined since 1983. Deficit spending is common. Abu Dhabi's oil income accounts for the bulk of federal revenues; under the constitution, each emirate contributes 50% of its net oil income to the federal budget.
The US Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) estimates that in 2000 the United Arab Emirates's central government took in revenues of approximately $20 billion and had expenditures of $22 billion. Overall, the government registered a deficit of approximately $2 billion. External debt totaled $12.6 billion.
The following table shows an itemized breakdown of government revenues and expenditures. The percentages were calculated from data reported by the International Monetary Fund. The dollar amounts (millions) are based on the CIA estimates provided above.
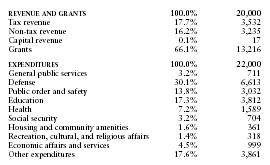
| REVENUE AND GRANTS | 100.0% | 20,000 |
| Tax revenue | 17.7% | 3,532 |
| Non-tax revenue | 16.2% | 3,235 |
| Capital revenue | 0.1% | 17 |
| Grants | 66.1% | 13,216 |
| EXPENDITURES | 100.0% | 22,000 |
| General public services | 3.2% | 711 |
| Defense | 30.1% | 6,613 |
| Public order and safety | 13.8% | 3,032 |
| Education | 17.3% | 3,812 |
| Health | 7.2% | 1,589 |
| Social security | 3.2% | 704 |
| Housing and community amenities | 1.6% | 361 |
| Recreation, cultural, and religious affairs | 1.4% | 318 |
| Economic affairs and services | 4.5% | 999 |
| Other expenditures | 17.6% | 3,861 |
Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: