Bhutan - Public finance
The largest category of annual current expenditure is public works, which presumably includes the maintenance of monasteries. Most of the annual budget deficit is covered by grants from India and from the UN and other international agencies. By 1996, Bhutan had achieved self-sufficiency in current expenses, thanks primarily to revenues from the Chhukha power project, Bhutan's largest hydro-electric plant.
The US Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) estimates that in 1995/1996 Bhutan's central government took in revenues of approximately $146 million and had expenditures of $152 million. Overall, the government registered a deficit of approximately $6 million. External debt totaled $245 million.
The following table shows an itemized breakdown of government revenues and expenditures. The percentages were calculated from data reported by the International Monetary Fund. The dollar amounts (millions) are based on the CIA estimates provided above.
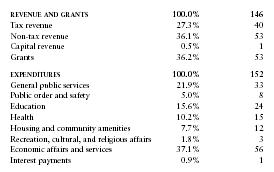
| REVENUE AND GRANTS | 100.0% | 146 |
| Tax revenue | 27.3% | 40 |
| Non-tax revenue | 36.1% | 53 |
| Capital revenue | 0.5% | 1 |
| Grants | 36.2% | 53 |
| EXPENDITURES | 100.0% | 152 |
| General public services | 21.9% | 33 |
| Public order and safety | 5.0% | 8 |
| Education | 15.6% | 24 |
| Health | 10.2% | 15 |
| Housing and community amenities | 7.7% | 12 |
| Recreation, cultural, and religious affairs | 1.8% | 3 |
| Economic affairs and services | 37.1% | 56 |
| Interest payments | 0.9% | 1 |
Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: