Grenada - Public finance
Main sources of revenue are export and import duties, income tax, estate duties, and various internal rates, licenses, and taxes. The 1986 Fiscal Reform Program replaced a number of taxes, including a personal income tax, with a VAT of 20% on certain consumer goods. In 1999, the government decided to double its expenditures on infrastructure projects, including airport expansion, the creation of a new port, and road construction.
The US Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) estimates that in 1997 Grenada's central government took in revenues of approximately $85.8 million and had expenditures of $102.1 million including capital expenditures of $28 million. Overall, the government registered a deficit of approximately $16.3 million. External debt totaled $196 million.
The following table shows an itemized breakdown of government revenues and expenditures. The percentages were calculated from data reported by the International Monetary Fund. The dollar amounts (millions) are based on the CIA estimates provided above.
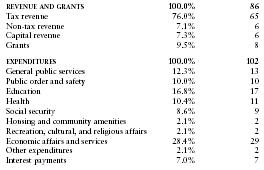
| REVENUE AND GRANTS | 100.0% | 86 |
| Tax revenue | 76.0% | 65 |
| Non-tax revenue | 7.1% | 6 |
| Capital revenue | 7.3% | 6 |
| Grants | 9.5% | 8 |
| EXPENDITURES | 100.0% | 102 |
| General public services | 12.3% | 13 |
| Public order and safety | 10.0% | 10 |
| Education | 16.8% | 17 |
| Health | 10.4% | 11 |
| Social security | 8.6% | 9 |
| Housing and community amenities | 2.1% | 2 |
| Recreation, cultural, and religious affairs | 2.1% | 2 |
| Economic affairs and services | 28.4% | 29 |
| Other expenditures | 2.1% | 2 |
| Interest payments | 7.0% | 7 |
Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: