Greece - Public finance
The state budget includes ordinary revenues and expenditures and a special investment budget administered by the Ministry of Coordination. The public sector, which employs 15% of the workforce, has many more civil servants than required for a country the size of Greece. Public payrolls, liberal social security benefits, and loss-generating state owned companies have all contributed to a government deficit. Recent austerity measures implemented to meet the criteria for European Monetary Union membership significantly lowered the budget shortfall.
The US Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) estimates that in 1998 Greece's central government took in revenues of approximately $45 billion and had expenditures of $47.6 billion. Overall, the government registered a deficit of approximately $2.6 billion. External debt totaled $63.4 billion.
The following table shows an itemized breakdown of government revenues and expenditures. The percentages were calculated from data reported by the International Monetary Fund. The dollar amounts (millions) are based on the CIA estimates provided above.
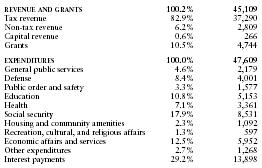
| REVENUE AND GRANTS | 100.2% | 45,109 |
| Tax revenue | 82.9% | 37,290 |
| Non-tax revenue | 6.2% | 2,809 |
| Capital revenue | 0.6% | 266 |
| Grants | 10.5% | 4,744 |
| EXPENDITURES | 100.0% | 47,609 |
| General public services | 4.6% | 2,179 |
| Defense | 8.4% | 4,001 |
| Public order and safety | 3.3% | 1,577 |
| Education | 10.8% | 5,153 |
| Health | 7.1% | 3,361 |
| Social security | 17.9% | 8,531 |
| Housing and community amenities | 2.3% | 1,092 |
| Recreation, cultural, and religious affairs | 1.3% | 597 |
| Economic affairs and services | 12.5% | 5,952 |
| Other expenditures | 2.7% | 1,268 |
| Interest payments | 29.2% | 13,898 |
Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: