Singapore - Foreign trade
Since World War II, Singapore has changed from an entrepôt center for the incoming and outgoing traffic of its neighbors in Southeast Asia to an exporting power in its own right. The leading exports of the mid-1960s—rubber, coffee, pepper, and palm oil—were replaced in the early 1980s by a variety of capital-intensive manufactures. Except for an occasional slowing, annual levels of trade regularly record double-digit expansion. During the late 1990s, expansion in the high-end manufacturing and services sectors began replacing capital-intensive production.
Most of the advanced electronics that Singapore exports also take up a substantial percentage of the world export market. The following chart shows the top eight exports:

| % OF COUNTRY TOTAL | |
| Automatic data processing equipment | 14 |
| Electronic microcircuits | 19 |
| Refined petroleum products | 9.4 |
| Telecommunications equipment | 4.3 |
| Organic chemicals | 2.2 |
| Circuit breakers | 2.4 |
| Sound recording tapes/discs | 1.8 |
| Optical equipment | 1.5 |
In 2000 Singapore's imports were distributed among the following categories:
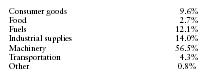
| Consumer goods | 9.6% |
| Food | 2.7% |
| Fuels | 12.1% |
| Industrial supplies | 14.0% |
| Machinery | 56.5% |
| Transportation | 4.3% |
| Other | 0.8% |
Singapore's main trading partners are the ASEAN group— principally Malaysia—the US, Malaysia, China and Hong Kong, and Japan. Principal trading partners in 2000 (in millions of US dollars) were as follows:

| COUNTRY | EXPORTS | IMPORTS | BALANCE |
| Malaysia | 25,026 | 22,832 | 2,193 |
| United States | 23,891 | 20,270 | 3,621 |
| China (inc. Hong Kong) | 16,216 | 10,627 | 5,589 |
| Japan | 10,400 | 23,154 | -12,754 |
| Thailand | 5,865 | 5,800 | 65 |
| Korea | 4,913 | 4,815 | 98 |
| Germany | 4,275 | 4,233 | 42 |
| United Kingdom | 3,550 | 2,736 | 814 |
| Philippines | 3,383 | 3,357 | 26 |
| Australia | 3,207 | 2,298 | 909 |