Algeria - Foreign trade
Crude oil and natural gas account for nearly all of Algeria's export value; industrial equipment and semi-finished goods and foodstuffs, especially wheat, dominate the country's imports. Surpluses accrued with the oil and gas price increases beginning in the mid-1970s and continuing through 1985, with the exception of 1978. In 1986, however, because of a severe drop in oil prices, Algeria experienced the first trade deficit since 1978 and the largest ever. The 1986 collapse of oil prices drove the government to implement decentralizing IMF programs in order to stabilize the economy. Algeria was able to register a trade surplus during most of the nineties, except during 1994, after a season of political turmoil. On 30 April 1998, the Algerian government chose not to re-subscribe to IMF structural programs. Coupled with low oil prices, this move brought about diminished export revenues, threatening a trade deficit. Rising oil prices during 1999 brought back a trade surplus. As of 2000, Algeria was running a trade surplus of nearly $13 billion (US dollars).
In 2000 Algeria's imports were distributed among the following categories:

| Consumer goods | 9.1% |
| Food | 24.8% |
| Fuels | 1.4% |
| Industrial supplies | 38.4% |
| Machinery | 24.2% |
| Transportation | 12.1% |
| Other | 0.0% |
Principal trading partners in 2000 (in millions of US dollars) were as follows:
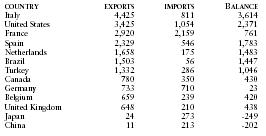
| COUNTRY | EXPORTS | IMPORTS | BALANCE |
| Italy | 4,425 | 811 | 3,614 |
| United States | 3,425 | 1,054 | 2,371 |
| France | 2,920 | 2,159 | 761 |
| Spain | 2,329 | 546 | 1,783 |
| Netherlands | 1,658 | 175 | 1,483 |
| Brazil | 1,503 | 56 | 1,447 |
| Turkey | 1,332 | 286 | 1,046 |
| Canada | 780 | 350 | 430 |
| Germany | 733 | 710 | 23 |
| Belgium | 659 | 239 | 420 |
| United Kingdom | 648 | 210 | 438 |
| Japan | 24 | 273 | -249 |
| China | 11 | 213 | -202 |
Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: